What are tags?
Tags are a feature in Git that can be used to make a snapshot of a repository from a point in time. It is generally used to mark releases (e.g. v1.2.4), and it functions as a shortcut to see what the repo looked like at the time.
What are releases?
Releases are a feature in Forgejo, independent of Git that allows you to attach files and release notes along with the source code at the time, and share it on Codeberg, linking to a Git tag.
Wait, what is the difference between tags and releases?
They are very similar, the difference being that tags are just the repository frozen in time and are part of Git (you can make a tag inside of Git), but releases are tags accompanied with a binary file and are not part of Git (you need to go to your Codeberg repository page to create a release).
Creating tags and releases
If you want to create tags, using Git is recommended. You can also create a new tag when creating a new release on Codeberg. Releases can be created using the Codeberg frontend or Codeberg's API — using Git to create new releases is not possible.
Tags are generally labelled by version numbers. It is good practice to prefix a version number with a v (e.g. v1.2.3)
and to use the Semantic Versioning specification for assigning and incrementing version numbers.
On Git
To create a tag using Git, use the following command in your local repository.
git tag -a <tag name> -m "<my tag message>"You can omit "<my tag message>" to write a longer tag message in an editor window.
Tags are not automatically pushed when you run git push (compared to commits or branches).
They have to be pushed manually to the remote target, like so:
git push --tags <remote target, probably "origin">The argument --tags pushes all local tags to the remote target. If you want to push only a specific tag, use:
git push <remote target, probably "origin"> <tag name, e.g., "v1.2.3">On Codeberg
To create a release on Codeberg, first go to your repository Settings, click on Units -> Overview,
enable Enable repository releases and click on Save setting.
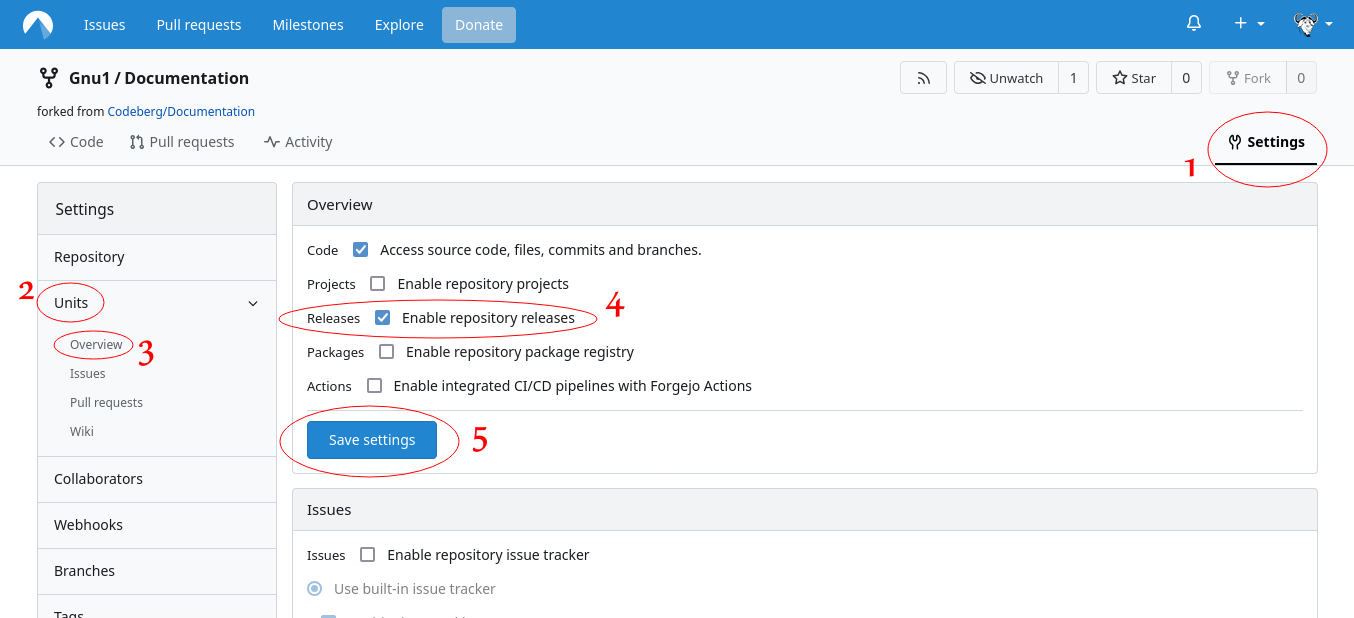
Then go to the Releases tab of your repository, and click on New Release:
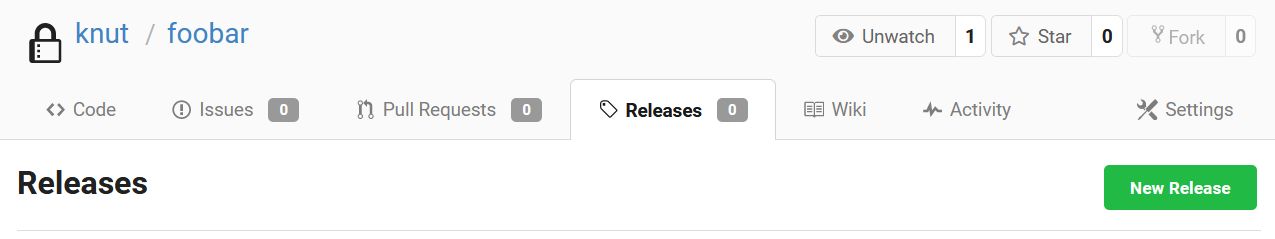
Here, enter a version number for your new release, select the branch that contains the code you want to release, and add a title and a description:
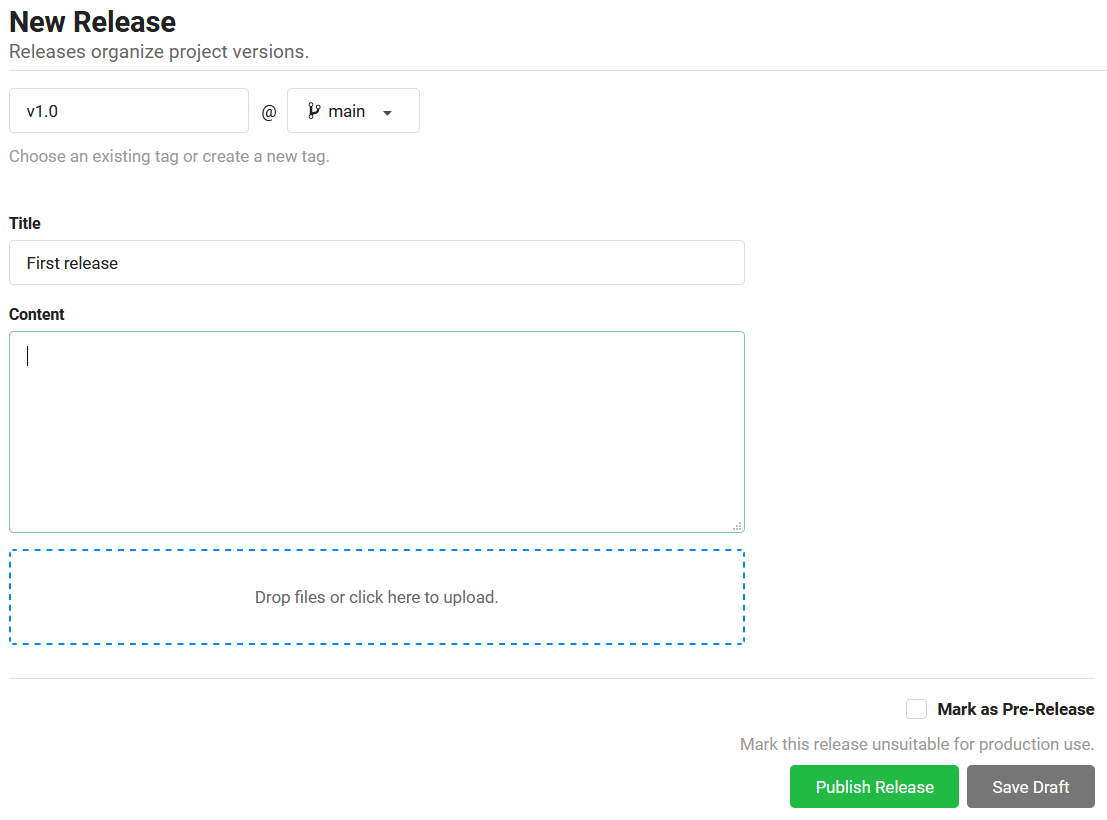
You can now either save it as a draft, or publish the release outright.
You are then re-directed to the Releases tab of your repository. The newly created release is now listed there:
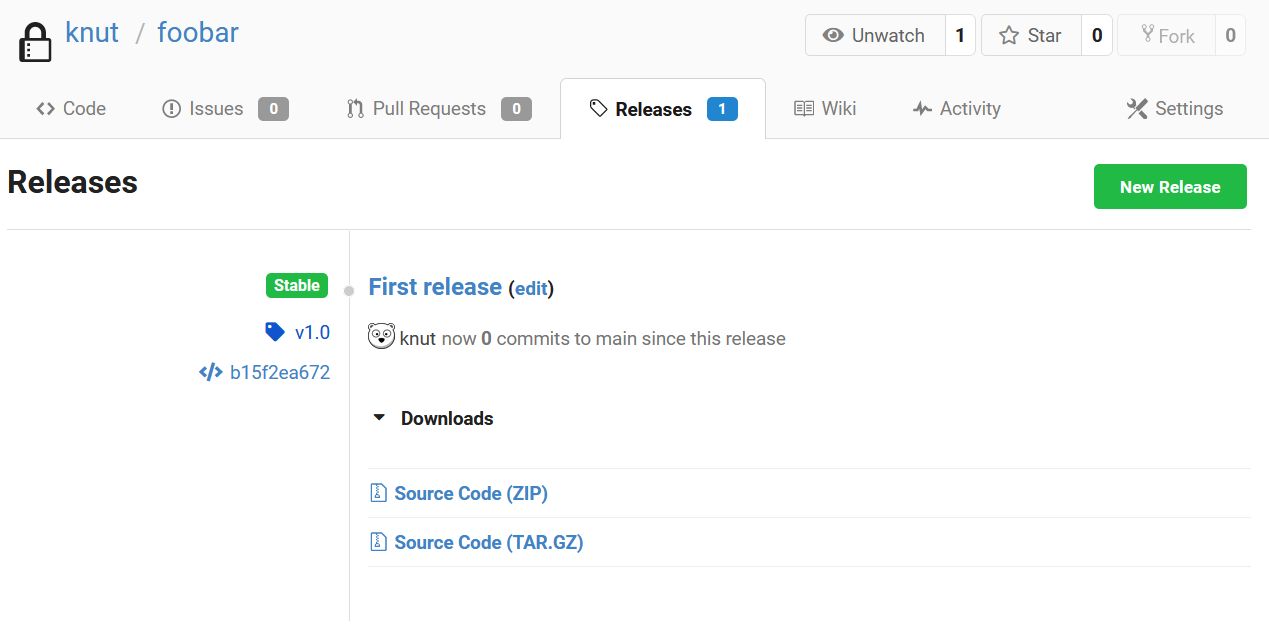
Here, you can edit the release if needed, and you can also download the source code in .zip or .tar.gz format.
Finding and viewing releases in a repository
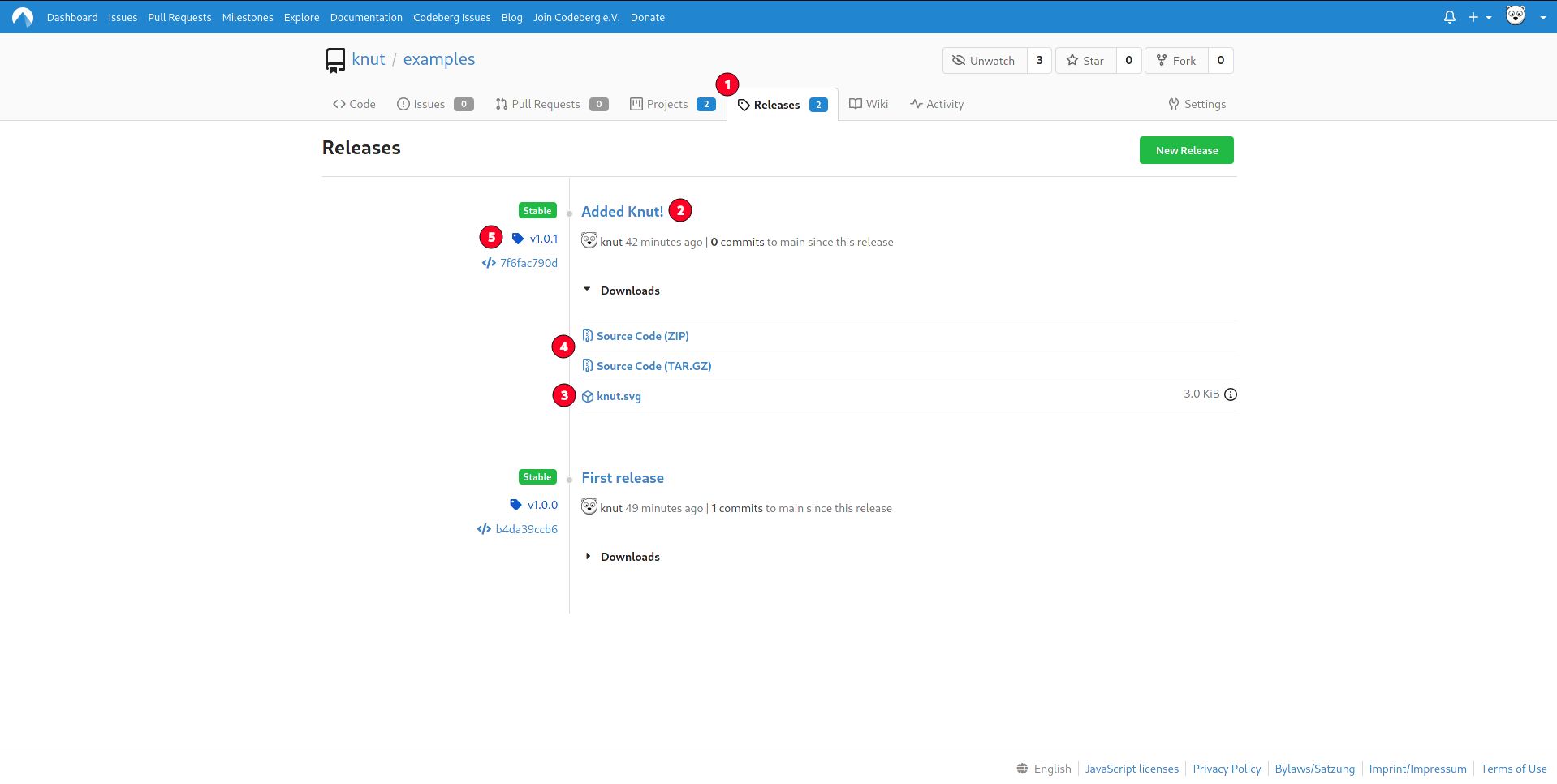
To view the release, go to the releases tab (1) in the repository. Then locate the release you want to view.
As an example, we will be looking at the Added Knut! release (2).
If you just want to access the files attached to the release, you can download it from the Downloads dropdown (3).
If you want to see a snapshot of the source code at the time of the release, select a source code archive download (4)
from the Downloads dropdown or click on the tag on the left side (5).